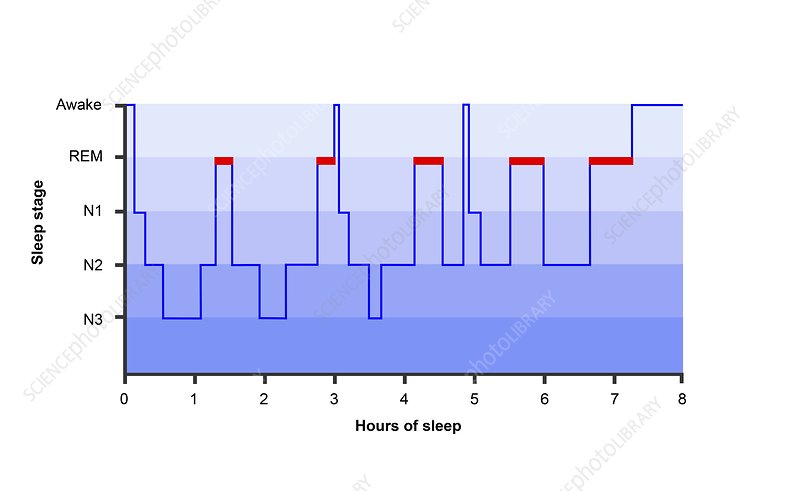
Sleep is a vital aspect of our overall well-being. It allows our bodies and minds to recharge and rejuvenate after a long day. However, the quality of our sleep can vary greatly from person to person. To better understand and analyze sleep patterns, scientists and researchers use a tool called a hypnogram. In this article, we will explore what a hypnogram is, how it works, and how it can provide valuable insights into your sleep architecture.
1. Introduction
Sleep plays a crucial role in our physical and mental health. It affects our cognitive functions, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. Understanding the different stages of sleep and their durations can provide valuable insights into our sleep patterns. One tool that helps in this analysis is the hypnogram.
2. What is a Hypnogram?
A hypnogram is a graphical representation of an individual’s sleep stages over a specific period. It visually displays the transitions between wakefulness, different stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. By examining a hypnogram, sleep specialists can gain a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s sleep architecture.
3. How is a Hypnogram Generated?
To create a hypnogram, sleep researchers utilize data obtained from polysomnography (PSG) studies. PSG involves monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, such as brain waves, eye movements, muscle activity, heart rate, and breathing patterns. These measurements are recorded using electrodes and sensors attached to the individual.
The data collected during a PSG study is then analyzed and scored by trained professionals. They review the recorded information in small time segments, usually 30-second epochs, and assign sleep stage labels to each epoch based on established criteria. This scoring process allows the creation of a detailed hypnogram.
4. Stages of Sleep
The hypnogram consists of different stages of sleep, each characterized by distinct brain wave patterns and physiological changes. Let’s explore the stages that make up a typical hypnogram:
Wakefulness
The hypnogram begins with the wakefulness stage. During this stage, the brain is highly active, and the individual is conscious and alert.
NREM Stage 1
NREM Stage 1 is the transition stage between wakefulness and sleep. It is a light sleep stage where the individual may experience drifting in and out of sleep. Brain waves during this stage are slower than wakefulness.
NREM Stage 2
NREM Stage 2 is the most prominent sleep stage in a hypnogram. It is characterized by a further decrease in brain activity, reduced muscle tone, and the appearance of specific sleep features like sleep spindles and K-complexes.
NREM Stage 3
NREM Stage 3 is often referred to as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep (SWS). It is a crucial stage for physical restoration and growth. During this stage, the brain exhibits slow delta waves, and it becomes harder to awaken the individual.
REM Sleep
REM sleep is the stage where most dreaming occurs. It is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and temporary paralysis of voluntary muscles. REM sleep is essential for cognitive functions and emotional regulation.
5. Analyzing Sleep Patterns
By studying a hypnogram, sleep specialists can extract valuable information about an individual’s sleep patterns. Here are some parameters that can be assessed using a hypnogram:
Sleep Efficiency
Sleep efficiency measures the percentage of time spent asleep out of the total time spent in bed. It helps determine how efficiently an individual is using their time in bed for sleep.
Sleep Latency
Sleep latency refers to the time it takes for an individual to fall asleep after lights out. It is an important measure of sleep onset and can be indicative of sleep disorders or other underlying issues.
Wake After Sleep Onset (WASO)
WASO measures the total time an individual spends awake during the night after initially falling asleep. It can be caused by factors such as insomnia, discomfort, or environmental disturbances.
REM Latency
REM latency measures the time it takes for an individual to enter the first REM sleep episode of the night. Deviations from the normal range can provide insights into certain sleep disorders.
Arousal Index
The arousal index quantifies the frequency of awakenings during the night. It helps evaluate the quality of sleep and detect potential disruptions that may affect overall sleep satisfaction.
6. The Importance of Sleep Quality
Understanding sleep quality is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being. A poor sleep pattern can lead to daytime sleepiness, cognitive impairment, mood disturbances, and an increased risk of various health conditions. Analyzing a hypnogram can aid in identifying sleep disturbances and guide appropriate interventions.
7. Factors Affecting Sleep Patterns
Several factors can influence an individual’s sleep patterns. Let’s explore some of the key factors:
Age
Sleep patterns change with age. Infants and young children require more hours of sleep, while adults typically need 7-9 hours. Older adults may experience changes in sleep architecture and a higher prevalence of sleep disorders.
Lifestyle Habits
Lifestyle habits such as irregular sleep schedules, excessive caffeine intake, and lack of physical activity can disrupt sleep patterns. Maintaining a consistent sleep routine and adopting healthy sleep habits can improve sleep quality.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions like sleep apnea, insomnia, restless leg syndrome, and psychiatric disorders can significantly impact sleep patterns. Proper diagnosis and treatment of these conditions are essential for restoring healthy sleep.
Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can lead to sleep difficulties, including trouble falling asleep and staying asleep. Relaxation techniques, stress management strategies, and creating a calming sleep environment can help alleviate these issues.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as noise, light, temperature, and uncomfortable bedding can disrupt sleep. Creating a sleep-friendly environment by minimizing disturbances and optimizing comfort can promote better sleep.
8. Conclusion
A hypnogram provides valuable insights into an individual’s sleep architecture and patterns. By analyzing the stages of sleep, sleep specialists can identify potential sleep disorders, evaluate sleep quality, and recommend appropriate interventions. Understanding your own sleep patterns can empower you to make informed decisions and prioritize healthy sleep habits for a better overall well-being.